Hey there, folks! Have you ever wondered what the fuss is all about when you hear the term “cloud computing”? Well, buckle up because we’re about to dive into the nitty-gritty of this tech phenomenon that’s shaking up the digital world.
What’s the Deal with Cloud Computing Anyway?
Alright, let’s break it down in simple terms. Cloud computing is like a magic portal on the internet that dishes out all sorts of digital goodies – from computers and storage to databases, software, and even some smarts to make sense of it all. Businesses these days are ditching the idea of hunkering down with their own data centers and instead, they’re grabbing what they need from remote servers managed by someone else. Yep, you heard that right – it’s like getting your tech resources delivered right to your digital doorstep.
The Scoop on Cloud Computing Goodies
Now, why is everyone jumping on the cloud bandwagon? Well, it’s not just a trend – it’s got some serious perks. First off, there’s the flexibility factor. Imagine having the power to scale up or down your resources exactly when you need them. Cloud computing lets you do just that. If your business suddenly decides to go big or go home, you can have more computing muscle in a snap. And if things quiet down a bit, you can scale back without breaking a sweat.
And let’s not forget about the financial magic that happens here. Think about the moolah you’d spend setting up your own fancy data center with all the whistles and bells. With cloud computing, you’re off the hook for those expenses. No need to spend sleepless nights worrying about hardware and maintenance. The cloud providers have got that covered for you.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The benefits of cloud computing include enhanced scalability, reliability, and flexibility. Organizations can promptly provide and de-provision resources as required, allowing them to respond quickly to shifting business requirements. Cloud computing can also save costs by reducing the expenses of constructing and operating on-site data centers, as well as the time and effort needed to manage those resources.
Cloud computing architecture is a fundamental aspect of how cloud computing works. It consists of a series of interconnected components that work together to deliver computing services over the Internet. This article provides an overview of cloud computing architecture and how it works, along with diagrams to facilitate understanding.
Breaking Down Cloud Computing Architecture
Alright, now that we’re all on the same page about cloud computing, let’s dig into the inner workings. Picture this: a bunch of puzzle pieces that fit together to create a virtual wonderland. This is what we call cloud computing architecture.
Understanding Cloud Computing Architecture
To better comprehend cloud computing architecture, let’s take a closer look at the three layers and their components.
Some of the components of the infrastructure layer include:
- Servers: Physical or virtual machines that host the computing services.
- Storage: Devices used to store data and files.
- Network: The physical and logical components used to connect the different components of the cloud system.
- Virtualization: Software that abstracts physical resources and makes them available as virtual resources.
Platform Layer
The platform layer provides a set of tools and services for developing and deploying applications. It abstracts the underlying infrastructure layer and provides a simplified interface for developers to work with.
Some of the components of the platform layer include:
- Operating System: The software that manages the resources of the servers.
- Application Server: Software that provides the runtime environment for applications.
- Database: Software used to store and retrieve data.
- Middleware: Software that connects different applications and components.
Application Layer
The application layer includes the applications that are delivered to end-users. This layer is responsible for providing a user-friendly interface and delivering computing services to the end user.
Some of the components of the application layer include:
- Web Applications: Applications that are delivered through a web browser.
- Mobile Applications: Applications that are delivered to mobile devices.
- APIs: Interfaces that allow different applications to communicate with each other.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDN): Networks that distribute content to users based on their geographic location.
Here is a diagrammatic representation of the cloud computing architecture:
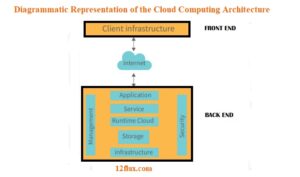
Service Models in Cloud Computing:
The three service models in cloud computing are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)

Here are their definitions with examples and diagrams:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS offers virtualized processing tools over the Internet, including servers, storage, and networking. The administration and upkeep of the virtual computers and apps that use the infrastructure are the responsibility of the cloud user with IaaS. The actual hardware, including servers, networking, and storage, is managed by the cloud service provider. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are a few examples of IaaS companies.
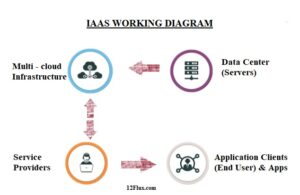
The above diagram shows the IaaS architecture where the cloud provider offers virtualized infrastructure resources, including servers, storage, and networking, to the cloud users. Cloud users can deploy their applications and services on top of the virtualized infrastructure using virtual machines and containers.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
PaaS provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications over the internet. With PaaS, the cloud user is responsible for developing and deploying their applications, while the cloud service provider manages the underlying infrastructure and platform. Examples of PaaS providers include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure.
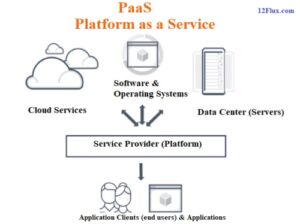
The above diagram shows the PaaS architecture where the cloud provider offers a platform for the cloud users to develop, test, and deploy their applications. The platform provides a complete development environment, including a runtime environment, development tools, and other services.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS provides software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install and run applications on their computers. With SaaS, the cloud service provider is responsible for managing and maintaining the software and underlying infrastructure, while the cloud user only needs to access the software through a web browser or app. Examples of SaaS providers include Salesforce, Dropbox, and Google Workspace.

The above diagram shows the SaaS architecture where the cloud provider offers software applications to the cloud users over the internet. The Cloud users can access the software applications through a web browser or app, and the cloud provider is responsible for managing and maintaining the software and underlying infrastructure.
Let’s now discuss which Cloud Computing Platform is Best. Azure and AWS are two of the most popular cloud computing platforms, which provide a range of cloud-based services, such as computing power, storage, and networking, that can be used by individuals and organizations.
Battle of the Cloud Titans: Azure vs. AWS
Alright, now that we’ve got the basics covered, let’s talk about the head-to-head matchup between two titans in the cloud computing realm – Azure and AWS.
Azure: Microsoft’s Crown Jewel
Azure is like a treasure trove of cloud-based goodness. From virtual machines to web apps, storage, and databases, it’s got it all. Developers are drawn to its compatibility with various programming languages, tools, and frameworks. It’s a playground for data storage, app development, and even IoT solutions.
AWS: Amazon’s Powerhouse
On the other side of the ring, we’ve got AWS – Amazon’s heavy hitter. It’s a one-stop shop for processing, storage, analytics, and more. With its scalability and adaptability, AWS is a top choice for websites, applications, and handling massive amounts of data.
The Verdict: Choosing Your Cloud Partner
So, what’s the final scoop on Azure vs. AWS? It’s a bit like choosing between chocolate and vanilla ice cream – both are delicious, but it depends on your taste.
What to Consider:
- Features and Services: Take a closer look at what each platform offers. While they’re similar, there might be some nuances that fit your needs better.
- Pricing: Money talks, right? Compare the pricing models to see which one won’t break the bank.
- Integrations: Check if your existing software plays nice with the cloud platform.
- Support: Make sure the level of support matches your needs.
- Community: If you’re into a lively community, see which platform has the most support from fellow cloud enthusiasts.
Wrapping Up the Cloud Chronicles
So there you have it, folks. Cloud computing isn’t just a buzzword – it’s a digital revolution that’s changing the game for businesses. Whether you’re team Azure or team AWS, the cloud offers a world of possibilities for those who dare to dream big. So go ahead, unleash your inner techie, and explore the cloud – it’s a wild ride you won’t want to miss!
Read Also: How to sell products on Amazon without inventory: Three Useful Methods 2023